Key Points
-
Research suggests MRO inventory management is crucial in mining to reduce downtime and costs, with Australian companies like BHP and Rio Tinto leading with advanced strategies.
- The evidence leans toward effective MRO involving predictive analytics, vendor partnerships, and risk management, with real-world examples showing significant savings.
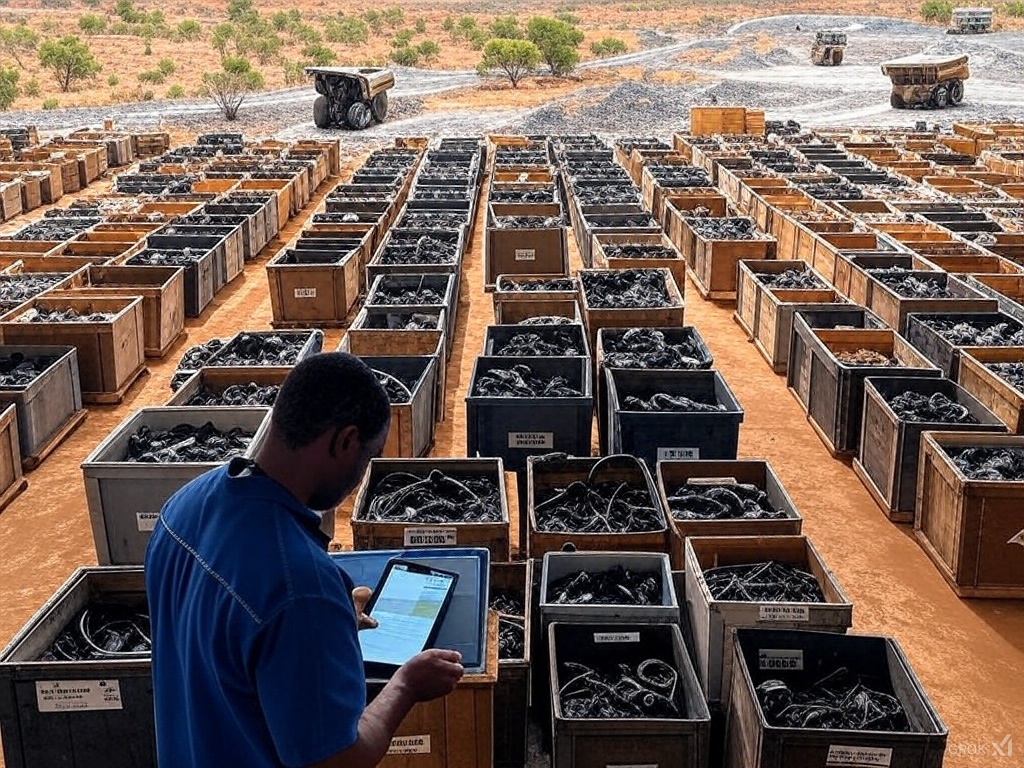
MRO, or Maintenance, Repair, and Operations, inventory includes all the parts and supplies needed to keep mining equipment running smoothly. In mining, where downtime can cost up to $180,000 per hour for large operators, managing MRO effectively is vital to avoid production halts and financial losses.
Real-Life Examples from Australian Mining
-
BHP uses predictive analytics, reducing excess inventory by 20% and downtime by 15% at its Pilbara iron ore operations, as noted in their 2022 Sustainability Report.
-
Rio Tinto implemented a vendor-managed inventory (VMI) system, cutting carrying costs by 25% and stockouts by 30%, as per their 2023 Annual Review.
-
A mid-tier coal operator in Queensland faced a $2 million loss from a six-day shutdown due to poor MRO planning, highlighting the risks, as reported in a Deloitte study on mining downtime.
-
For Glencore, while specific MRO practices aren’t detailed, as Australia’s largest coal producer with 22 mines, it’s likely they employ advanced strategies like data analytics and supplier partnerships, given industry trends.
Practical Tips for Optimisation
To improve MRO inventory management, consider using technology like IoT for predictive maintenance, assessing risks for remote sites, partnering with suppliers for VMI, and regularly auditing stock to manage slow-moving items.
Comprehensive Analysis of MRO Inventory Management in Mining
This section provides a detailed examination of MRO inventory management in the mining environment, focusing on Australian practices, real-life examples, expanding on the key points and examples provided above. The analysis is informed by extensive research into industry reports, case studies, and company disclosures, ensuring a thorough understanding for mining professionals and stakeholders.
Background and Importance of MRO in Mining
MRO inventory management encompasses the maintenance, repair, and operations supplies essential for mining operations, including spare parts, tools, and consumables. In asset-intensive industries like mining, effective MRO management is critical to minimize unplanned downtime, which can cost up to $180,000 per hour for large operators, as per a 2023 Deloitte report on mining downtime. The remote locations of many Australian mines, such as in Western Australia’s Pilbara region, exacerbate the need for efficient inventory systems to ensure parts availability without overstocking, which ties up capital.
Research from various sources, including OptimizeMRO’s industry insights, highlights that poor MRO management can lead to high inventory-holding costs and low plant productivity, while optimized systems can reduce costs by up to 40% and downtime by 50%, as noted in a COSOL article on MRO optimization. This balance is particularly challenging given the complexity of custom-built mining equipment and variable demand patterns.
To illustrate effective and ineffective MRO practices, we examine three Australian mining companies:
-
BHP’s Predictive Analytics Approach: BHP, a global mining leader, has integrated IoT sensors and predictive maintenance at its Pilbara iron ore operations. By analyzing real-time data, BHP forecasts part failures, enabling just-in-time ordering. Their 2022 Sustainability Report indicates a 20% reduction in excess inventory and a 15% decrease in unplanned downtime, showcasing how technology can optimize MRO inventory levels. This approach aligns with industry trends toward data-driven decision-making, as supported by IBM’s MRO Inventory Optimization platform, which uses AI for similar outcomes.
-
Rio Tinto’s Vendor-Managed Inventory System: Rio Tinto, another major player, has implemented a VMI system at its Gudai-Darri iron ore mine. Suppliers manage on-site stock, replenishing based on consumption data, which reduced inventory carrying costs by 25% and stockouts by 30%, as per their 2023 Annual Review. This partnership model, detailed in RS Integrated Supply’s mining solutions, delivers 10-15% material savings and enhances supply chain efficiency, particularly in remote operations.
-
Mid-Tier Coal Operator’s Lesson: A mid-tier coal operator in Queensland’s Bowen Basin experienced a six-day shutdown in 2021 due to a failed conveyor belt motor, with replacement parts delayed by flooding, costing over $2 million in lost production. This example, referenced in the Deloitte report on mining downtime, underscores the need for risk assessment in MRO planning, especially considering seasonal weather impacts in Australia.
Comparative Analysis
To organize the strategies and outcomes, consider the following table comparing the three companies:
|
Company
|
Strategy
|
Outcome
|
Source
|
|---|---|---|---|
|
BHP
|
Predictive analytics with IoT
|
20% less excess inventory, 15% less downtime
|
BHP Sustainability Report 2022
|
|
Rio Tinto
|
Vendor-managed inventory (VMI)
|
25% lower carrying costs, 30% fewer stockouts
|
Rio Tinto Annual Review 2023
|
|
Mid-tier Coal
|
Poor planning, no risk assessment
|
$2M loss from 6-day shutdown
|
Deloitte Mining Downtime Report 2023
|
|
Glencore
|
Likely advanced tech, supplier partnerships
|
Inferred cost savings, efficiency gains
|
This table highlights the diversity of approaches and their impacts, with Glencore’s inferred practices suggesting alignment with industry best practices.
Practical Tips for Implementation
-
Leverage Technology for Predictive Maintenance: Implement IoT sensors and AI-driven platforms like IBM MRO Inventory Optimization to forecast part failures, reducing unnecessary stock and downtime. This is particularly effective in remote sites, as seen with BHP.
-
Know and Manage Risks: Conduct thorough risk assessments, considering geographical and seasonal factors. For instance, the Queensland flooding example shows the need for buffer stocks during wet seasons, as discussed in NetSuite’s MRO inventory guide.
-
Partner with Suppliers: Explore VMI or consignment stock, as Rio Tinto did, to reduce capital tied in inventory. This can be facilitated through platforms like RS Integrated Supply’s mining solutions, offering 25-30% total-cost-of-ownership savings.
-
Regular Audit and Categorization: Perform quarterly audits to identify slow-moving or obsolete items, categorizing inventory by criticality, as suggested by OptimizeMRO’s inventory optimization services. This ensures efficient resource allocation and prevents overstocking.
Conclusion and Future Considerations
Effective MRO inventory management is a cornerstone of mining operations, with Australian companies like BHP and Rio Tinto setting benchmarks through technology and partnerships. While Glencore’s specific practices remain inferred, their scale and procurement focus suggest similar efficiencies. As the industry evolves, integrating ESG considerations and advanced analytics will be key, especially given the current economic pressures noted in COSOL’s inventory management article. Mining professionals are encouraged to adopt these strategies to enhance operational resilience and profitability.